
A cataract is a clouding in the clear lens of your eye. For people who have cataracts, seeing through cloudy lenses is a bit like looking through a frosty or fogged-up window. Clouded vision is a cause of cataracts which makes it more difficult to read, drive a car (especially at night) or see the expression on a friend’s face.
Most cataracts develop slowly and do not disturb a person’s eyesight early on. But eventually, they interfere with your vision with time.
In the early stage, stronger lighting and eyeglasses can help you deal with cataracts. But if impaired vision interferes with your usual activities, there might be a need for cataract surgery.
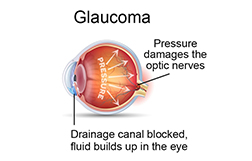
Glaucoma surgery procedures are intended to achieve one of two basic results: decrease the production of intraocular fluid or increase the outflow (drainage) of this same fluid. Without treatment, glaucoma can also result in total permanent blindness within a few years.
Most people with glaucoma experience no early symptoms or pain. A patient needs to see an eye doctor regularly so he/she can diagnose and treat glaucoma before a long-term visual loss happens.
If you’re above 40 years and have a family history of the disease, you should get a complete eye test from an eye doctor every 1 to 2 years. If you have any health problems like diabetes or a family history of glaucoma or you are at a risk for other eye diseases, you may need to go more often.
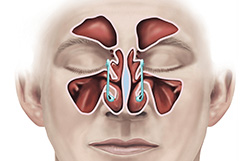
Sinus Surgery is a process through which your Doctor aims to open the pathways of the sinuses and clear blockages. This is an option for people with who have ongoing and recurrent sinus infections, or for the people with abnormal sinus structure, or abnormal growths in the sinus. Sinus surgery is the last resort that is often attempted when other treatments and procedures doesn’t work. A Sinus Surgery is performed with little discomfort. It is a small procedure that has few complications.
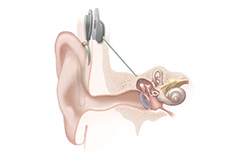
A Cochlear Implant uses a sound processor that fits behind the Ear. It is an electronic device that partly restores hearing which can be an option for people who have severe hearing loss from inner-ear damage and who receive limited benefit from hearing aids. This processor captures sound signals and transmits them to a receiver implanted under the skin behind the ear. The signals arouse the auditory nerve, which then directs them to the brain. The brain interprets those signals as sounds, though these sounds won’t be just like normal hearing. It will take some time and training to learn to interpret the signals received from a cochlear implant. Within a year of use, most of the people with cochlear implants make considerable gains in understanding speech.

IVF or In Vitro Fertilization treatment is an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) that is the process of fertilization by extracting eggs, retrieving a male sperm sample, and then manually combining an Egg and Sperm in a laboratory dish. After that the embryo(s) is then transferred to the uterus. Other forms of ART include gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT) and Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT).
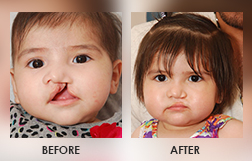
Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate is a physical split or separation of the two sides of the upper lip and appears as a narrow opening or gap in the skin of the upper lip. They are facial and oral malformations that occur very early in pregnancy, while the baby is developing inside the mother’s womb. Clef ting results when there is less tissue in the mouth or lip area, and the tissue that is available does not join together properly.
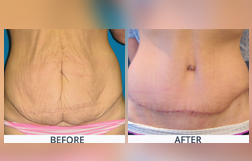
Abdominoplasty also known as tummy tuck is a cosmetic surgical procedure to improve the appearance of the abdomen. In this procedure a surgeon removes the excess skin and fat from the abdomen. Other connective tissue in the abdomen (fascia) usually is tightened with sutures as well. The remaining skin is then repositioned to create a more toned look that can improve the appearance of a person.
A person may choose to have a tummy tuck or an Abdominoplasty surgery if he/she has excess fat or skin around the area of bellybutton or a weak lower abdominal wall. A tummy tuck can also help in boosting body image.
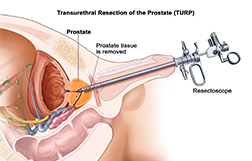
Traditionally, TURP or Transurethral resection of the prostate has been considered the most effective treatment for an enlarged prostate. A TURP is a surgical procedure that is followed by cutting away a section of the prostate. The prostate is located between the penis and bladder, and surrounds the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the penis is a small gland in the pelvis only found in men. It’s). If the prostate becomes enlarged, it can put pressure on the bladder and urethra which can cause symptoms that affect urination.

A Cosmetic Surgery is a type of plastic surgery that aims to improve a person’s appearance, but it should be approached with caution. The procedures for a cosmetic surgery are available for almost any part of the body, but the choice to undergo cosmetic surgery should not be taken lightly. The results of such surgeries are often permanent, so it is important to be sure about the decision, to use an appropriate practitioner, and to have the right motivation. A Cosmetic surgeon may refer a patient for counselling before he/she undergoes the surgery if they believe there is an underlying problem that cannot be solved by the surgery, or if the patient shows signs of Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD).
BDD can cause a person to perceive that there is something seriously wrong with his/her appearance, when objective evidence suggests otherwise.
Reconstructive Surgery is another type of plastic surgery or cosmetic surgery. It aims to improve function and to give a normal appearance to a part of the person’s body that has been damaged, for example, after a mastectomy.
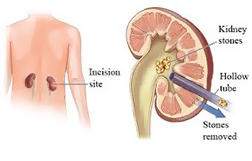
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a procedure that is used to remove kidney stones from the body when they can’t pass on their own. A scope is inserted through a small incision in your back to remove the kidney stones. This treatment is often performed when a person has larger stones or when other procedures, such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy or uteroscopy, are unsuccessful or not possible then percutaneous nephrolithotomy is done.
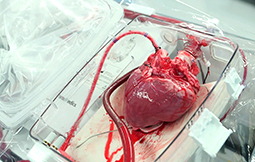
Heart transplant surgery is a procedure typically performed on patients with end-stage heart failure. In a heart transplant surgery or cardiac transplant a damaged heart is replaced with a healthy one. The most common procedure of this surgery is by replacing the functioning heart of an ‘organ donor’ and implanting it into the patient. Patient’s own heart is either removed or replaced with the donor’s heart or, much less commonly, the recipient’s diseased heart is left in place to support the donor’s heart.
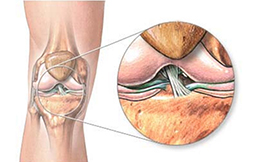
An Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) injury is a tear or sprain of the anterior cruciate (KROO-she-ate) ligament (ACL). It is one of the major ligaments in your knee. Most commonly ACL injuries occur during sports that involve sudden stops or changes in direction, jumping and landing — such as soccer, basketball, football and downhill skiing. Many people usually hear or feel a “pop” in the knee when an ACL injury occurs. Your knee may also swell, feel unstable and become too painful to bear any kind of weight.
Depending on the severity of your ACL injury, treatment may include rest and rehabilitation exercises for a few days to help you regain strength and stability or in some case surgery is also recommended to replace the torn ligament followed by rehabilitation. A proper training program may help and reduce the risk of an ACL injury.
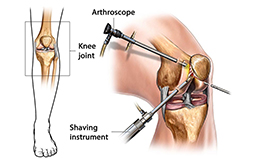
Knee arthroscopy is a surgical procedure in which the doctors view the knee joint without making any large incision (cut) through the skin and other soft tissues. This procedure is used to diagnose and treat a wide range of knee problems. During a knee arthroscopy procedure, the surgeon inserts a small camera, called an arthroscope, into the knee joint. The camera that is inserted will show pictures on a video monitor, and then the surgeon uses these images to guide miniature surgical instruments. As the surgical instruments and the arthroscopy are thin, the surgeon can use very small incisions, rather than the larger incision needed for open surgery. This results in less pain for the patients, less joint stiffness, and often shortens the time it takes to recover and return back to normal activities.
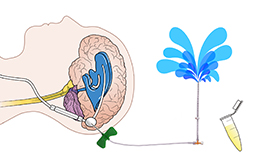
Placements of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) shunt are commonly used to treat hydrocephalus. These shunt sy s drain excess fluid from the brain to the other part of the body where the fluid is absorbed as part of the circulatory process. The swelling of the brain due to excess buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a medical procedure that relieves pressure on the brain that is caused by fluid accumulation. The procedure is done when there is too much pressure in the brain caused due to CSF accumulation, a medical condition called hydrocephalus. It mostly occurs in babies and older adults.
Normally, cerebrospinal fluid flows through the ventricles of the brain, thereby immersing the brain and spinal cord in it and eventually gets absorbed in the blood. When this normal flow is interrupted, it causes fluid accumulation and puts harmful pressure on brain tissues. VP Shunt drains fluid from the brain to other parts of the body where the fluid is absorbed.
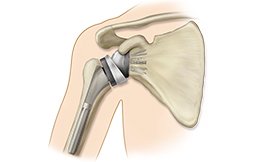
A shoulder Replacement surgery involves removing the injured parts of the shoulder and replacing it with the artificial components, called prosthesis. The treatment options are either the replacement of just the head of the humerus bone (ball), or replacement of both the ball and the socket (glenoid). In this surgery the damaged humeral head (or joint “ball”) is replaced with a metal ball, and the surgeon put a new smooth plastic surface on the glenoid (called the “socket”). Metal on the plastic surfaces (rather than metal on metal) are the hallmark of virtually all shoulder replacement implant sy s. Partial shoulder replacement (or hemi-replacement) may also be indicated with certain complex shoulder fractures of the humeral head. This procedure requires the replacement of the ball component wholly.
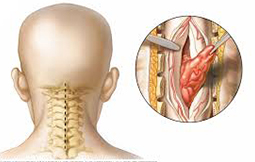
Spinal tumors are a various collection of lesions ranging from benign (non-cancerous) tumors treated with surgical resection, to malignant (cancerous) tumors that require multidisciplinary care involving surgery, radiation and/or chemo . Benign spinal tumors of the spine include neurofibromas, schwannomas, and meningiomas. These tumors mostly occur inside the spinal canal, but outside the spinal cord itself. The spinal tumors are most often treated with surgical resection alone, although the complex cases may also require additional such as radiation or chemo .
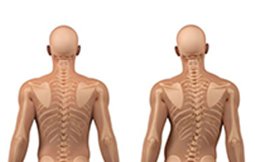
Scoliosis is a kind of disorder that causes an abnormal curve of the spine, or backbone. There is a normal spinal curve when looked from the side, but it should appear straight when looked from the front. Kyphosis is a curve caused in the spine seen from the side in which the spine is bent forward. There is a normal kyphosis in the middle also known as thoracic spine. Lordosis is a curve that is seen from the side in which the spine is bent backward. There is a normal lordosis in the upper or cervical spine and the lower spine or the lumbar spine. People with scoliosis often develop additional curves to any side of the body, and the bones of the spine twist on each other, forming a C or an S-shaped or scoliosis curve in the spine.
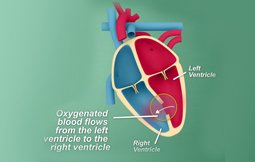
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) is a congenital heart problem where there is a hole created in the walls that divide the lower chambers of the heart commonly known as a hole in the heart. A VSD surgery is performed to treat this defect in one of the following ways:
Intra-Cardiac Technique – This type of technique is a more common open-heart surgery technique where a machine takes over the functions of the heart and lungs. This type of technique is usually performed along with a cardiopulmonary bypass.
Transcatheter Technique – This technique is comparatively more complicated procedure that involves the use of some surgical instruments that are passed through the catheters and attached to the large blood vessels of the heart.
If you’re considering the option of traveling for a ventricular septal defect treatment in India, we will be happy to help you find the right doctors and answer all your queries.
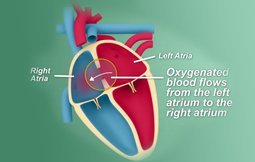
An Atrial Septal Defect (ASD), also called as a hole in the heart is a congenital heart defect, usually present in newborns since birth. This is a type of congenital heart defect when there is a hole in the upper chamber of the heart, an atrial septal defect surgery is required to treat this problem. Though this condition is present since birth, small defects might close automatically during infancy or early childhood. However, the large and long-lasting defects can cause damage to the patient’s heart and lungs, making it imperative to treat it at the right time. For adults living without the diagnosis of ASD since decades, there are higher chances of heart failure or high blood pressure which can ultimately affect the arteries in the lung.
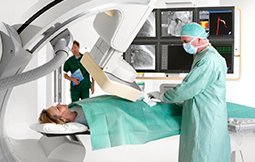
A coronary angiography is a test that uses medical imaging to view the organs and blood vessels of the patient’s body to find out if you have a blockage in a coronary artery. The test is done by using an X-Ray based technique, like fluoroscopy (Immediately obtains moving pictures using X-Ray). Your doctor will be concerned that you’re at risk of a heart attack in case you have unstable angina, atypical chest pain, aortic stenosis, or unexplained heart failure. During the test a contrast dye will be injected into the arteries with the help of a catheter (thin, plastic tube), while your doctor watches how blood flows through your heart on an X-ray screen. It is also known as a cardiac angiogram, catheter arteriography, or cardiac catheterization.
Based on the results of the test, your doctor may decide that you would benefit from having coronary angioplasty or stenting to help clear clogged arteries. To prevent needing another procedure it’s also possible that the following treatments could be done during your angiography:
Coronary Angioplasty: It is a non-surgical procedure to widen blocked or narrowed coronary arteries, and restore the blood flow to the heart muscles. It is performed to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. These blood vessels are called the coronary arteries. Typically, a catheter placed on a guide wire is inserted inside the blocked artery to help widen it. Angioplasty is also known as Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) and Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA).
Stenting: In this procedure a tiny tube called stent is inserted into a blocked passageway to keep it open. This stent restores the flow of blood or other fluids, depending on where it’s placed. These stents are made of either metal or plastic. Stent grafts are larger stents used for larger arteries that may be made of a specialized fabric. Stents can also be coated with the help of medicines to help keep a blocked artery from closing.




















